This is one of the confusing topics for me but now I have completely understood. There are lots of blog posts on this with different perspectives and now I am also adding my perspective too. Hope this will help you to understand the concept.
What is a port?
Port is a virtual interface in the operating system that is used for sending and receiving TCP/UDP packets from the same system or another system. Applications interact by using a port number like SSH port 22.
What is port forwarding?
In simple language, port forwarding means redirecting the TCP packets from one IP address and port number to another IP address and port number.
Example: Let's assume you have a system in your house behind the router. No public IP address is assigned to your system directly. Now you want to access that system from another network by using SSH.
How will you do that?
Solution: You do the port forwarding in your router, where you map the router port to your system port and IP address, in this scenario with port 22 (SSH).
Router public IP address: 49.36.222.180
Router port used for mapping with the system IP address and port 22: 1337
When users from another network try SSH connection by using public IP address and port1337, the router redirects this connection to your system port 22 and it gives access to your system which is behind the router.
Types of port forwarding:
- Local port forwarding
- Remote port forwarding
- Dynamic port forwarding
Before understanding the difference between local and remote port forwarding, understand that local and remote terminology changes as per the:
- Depends on the service which you want to access on your system from another system or you want to give access of the service from your system to another system.
- Where you want to use your SSH password
Local port forwarding
Local port forwarding means when you map your IP address and port with the IP address and port of another system of which service you want to access. So when you request for service by your IP address and port which you used for mapping, it redirects the request to another system IP address and port.
Example:
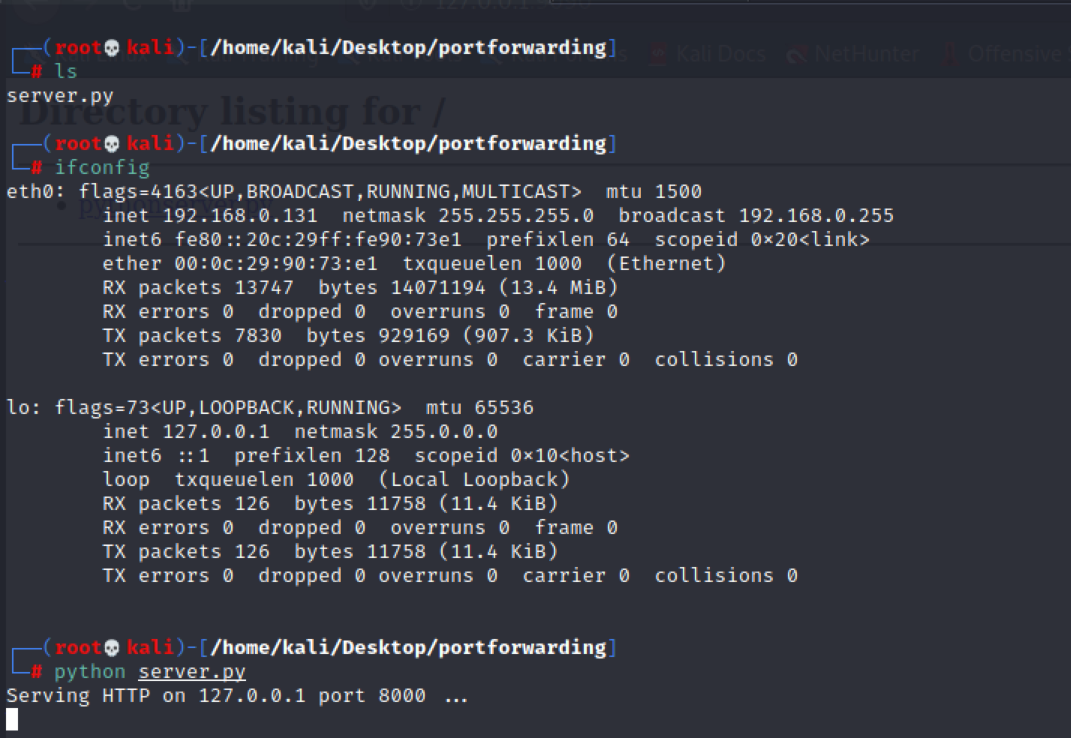
Victim System (V) (127.0.0.1:8000): The HTTP service is running on IP address 127.0.0.1 and port 8000
Attacker System (A) (192.168.0.195:80): Attacker has access of the victim system, the attacker knows the SSH credential of the victim but the HTTP services running on 127.0.0.1 of the victim system. The attacker wants to access that service by the attacker machine so that he can run Nmap script scan on the HTTP port because the attacker doesn’t have access to install any software on the victim machine.
So, in this scenario, you are the attacker. You want to access the HTTP service by your system. In this case, we are going to use local port forwarding because we have victim SSH credentials and we want to run a Nmap scan on the HTTP service from our system.
We want to access the HTTP service by our own system.
Please note we can access the HTTP service by using remote port forwarding also but in that scenario, we need to enter the SSH credentials of the attacker machine on the victim machine. Which is not best practice. As I told you it depends on the scenarios how you are using it you can get access by any approach.
Command:
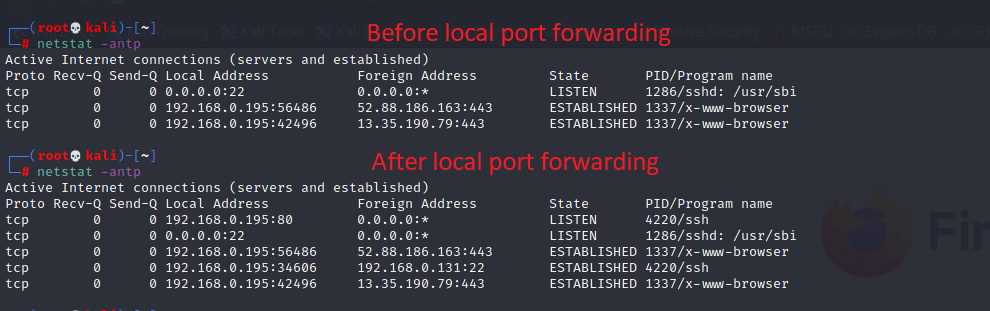
ssh -N -L 192.168.0.195:80:127.0.0.1:8000 root@192.168.0.131 -p 22
or
ssh -N -L 80:127.0.0.1:8000 root@192.168.0.131 -p 22 (In this case attacker want to access by 127.0.0.1)
- -N: It tells SSH to not start a shell and only forward ports.
- -L: It is used for local port forwarding.
- 192.168.0.195:80: It’s the attacker's IP address and port used for mapping it with the victim's IP address and port.
- 127.0.0.1:8000: It’s the victim’s IP address where the HTTP service is running.
- root@192.168.0.131: It’s the victim’s machine IP address and username for SSH.
- -p 22: It’s the SSH port using for SSH connection.
POC’s:
Victim Machine (192.168.0.131):
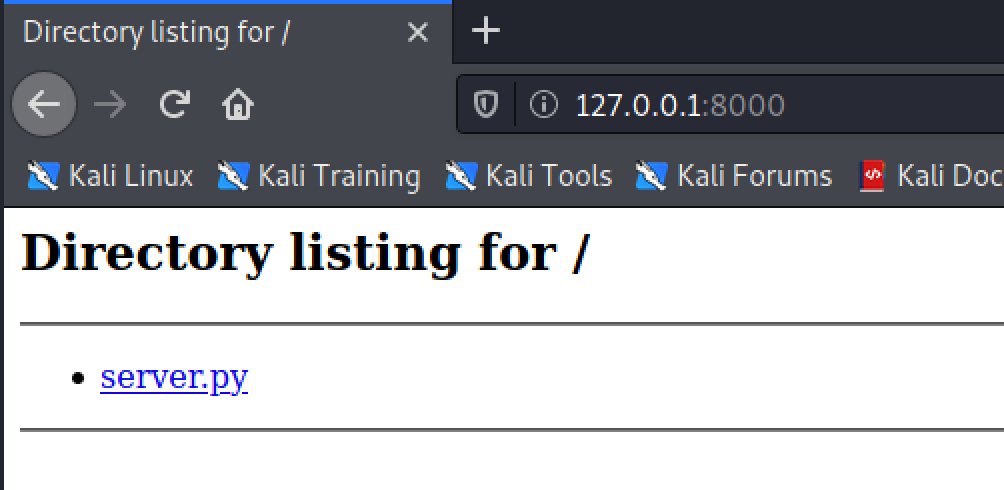
Attacker Machine (192.168.0.195):


Remote port forwarding
Remote port forwarding is the opposite of local port forwarding. It’s not mostly used.
Remote port forwarding means when you open the port from the system where the service is running into the system where you want to access the service. Check the below example where you run the SSH command in the victim system and open the port into the attacker machine, when the attacker uses the IP address and that port number (port: 80) the request is redirected to port 8000 of the victim machine.
Please note that here in this scenario we are running the SSH command from the system where the service is running and using the SSH credentials of the system who want to access the service.
Example:
We are using the same example as above the difference is that the SSH command executes in which system is changed but in this case also the attacker is able to access the victim's HTTP service but the attacker need to put their SSH credentials in the victim machine as I told you the concept is change as per the command execution.
Victim System (V) (127.0.0.1:8000): The HTTP service is running on IP address 127.0.0.1 and port 8000
Attacker System (A) (192.168.0.195:80): Attacker has access of the victim system, the attacker knows the SSH credential of the victim but the HTTP services running on 127.0.0.1 of the victim system. The attacker wants to access that service by the attacker machine so that he can run Nmap script scan on the HTTP port because the attacker doesn’t have access to install any software on the victim machine.
So, in this scenario, you are the attacker. You want to access the HTTP service by your system. In this case, we are going to use remote port forwarding because we have victim SSH credentials as well as we know our own system credential and because of some reason we are not able to use local port forwarding.
Command:
ssh -N -R 80:127.0.0.1:8000 root@192.168.0.195 -p 22
- -N: It tells SSH to not start a shell and only forward ports.
- -R: It is used for remote port forwarding.
- 80: It’s the victim’s port that is forward to the attacker's machine. Do netstat -antp, the 80 port is visible in the attacker machine.
- 127.0.0.1:8000: It’s the victim’s IP address where the HTTP service is running.
- root@192.168.0.195: It’s the attacker's machine IP address and username for SSH.
- -p 22: It’s the SSH port using for SSH connection.
POC’s:
Victim Machine (192.168.0.131):

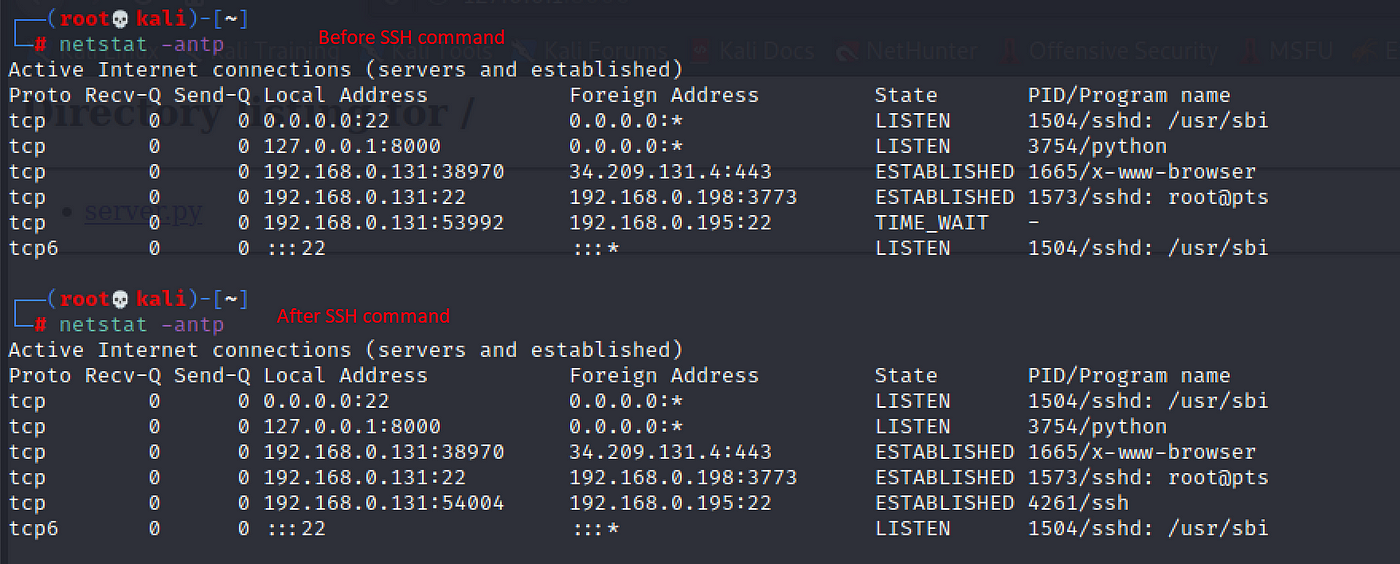
Attacker Machine (192.168.0.195):
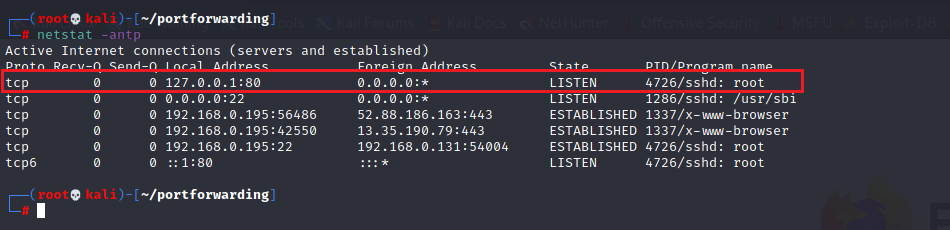
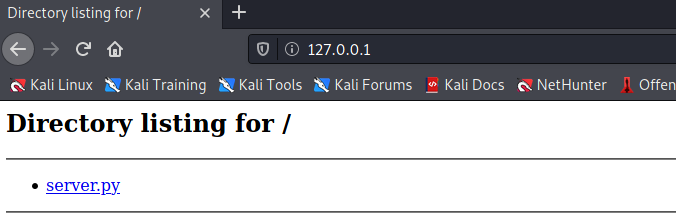
Dynamic port forwarding
Dynamic port forwarding allows you to create a proxy server on the machine that is used as an SSH server.
SSH Client: From where you initiate the SSH connection.
SSH Server: The machine whose password you used in the SSH client.
In dynamic port forwarding, you can use the IP address and port as a proxy like you use your Burp proxy.
Example:
Let assume that you have access of the victim machine by SSH when you enumerate you find that there is a website in the same network which is accessible by the victim machine but not by the attacker machine. So if the attacker wants to access that website by the attacker machine, one way is to create the dynamic port forwarding from the attacker machine and add that IP address and port in the browser SOCKS5 proxy. When an attacker tries to access that URL that was not accessible before, it is now accessible because the request sends to the proxy IP, port and from that proxy address it forwards to the destination URL which is accessible from the proxy server machine.
Command:
ssh -N -D 8080 root@13.234.34.153
Victim IP (13.234.34.153): Act as a proxy server
Attacker public IP (49.36.222.189): Act as a client. who want to access the resource.
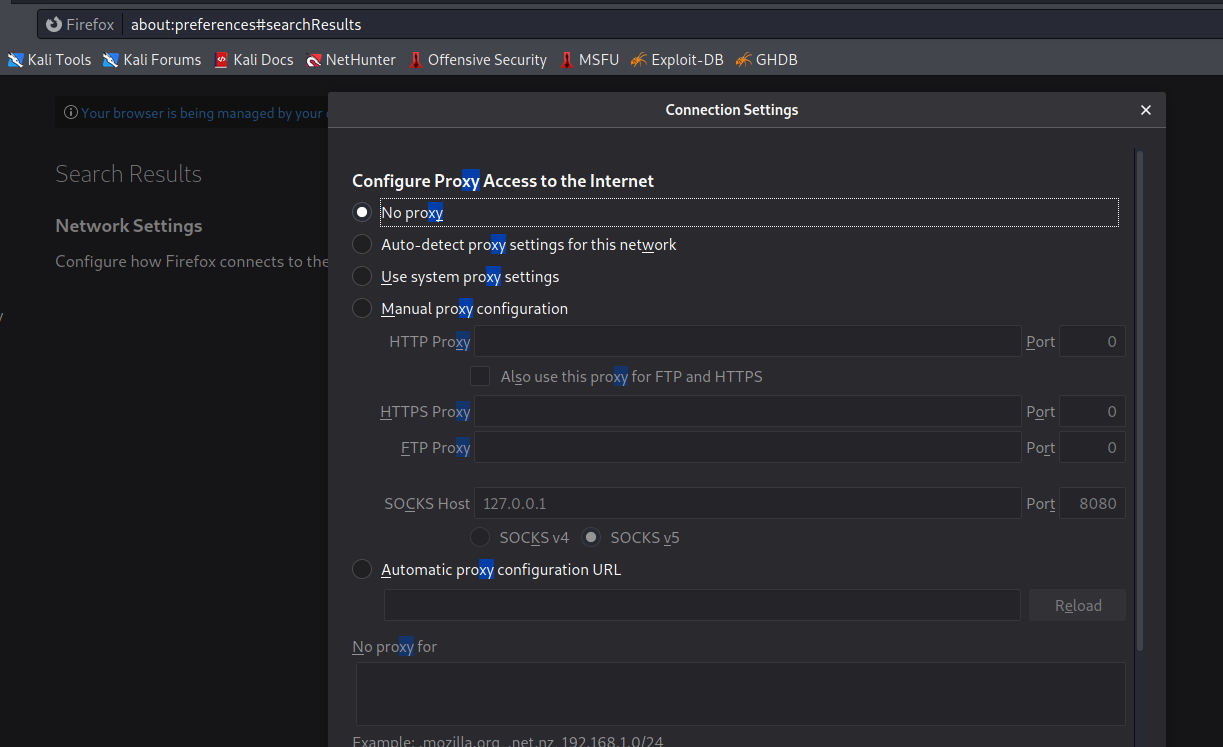
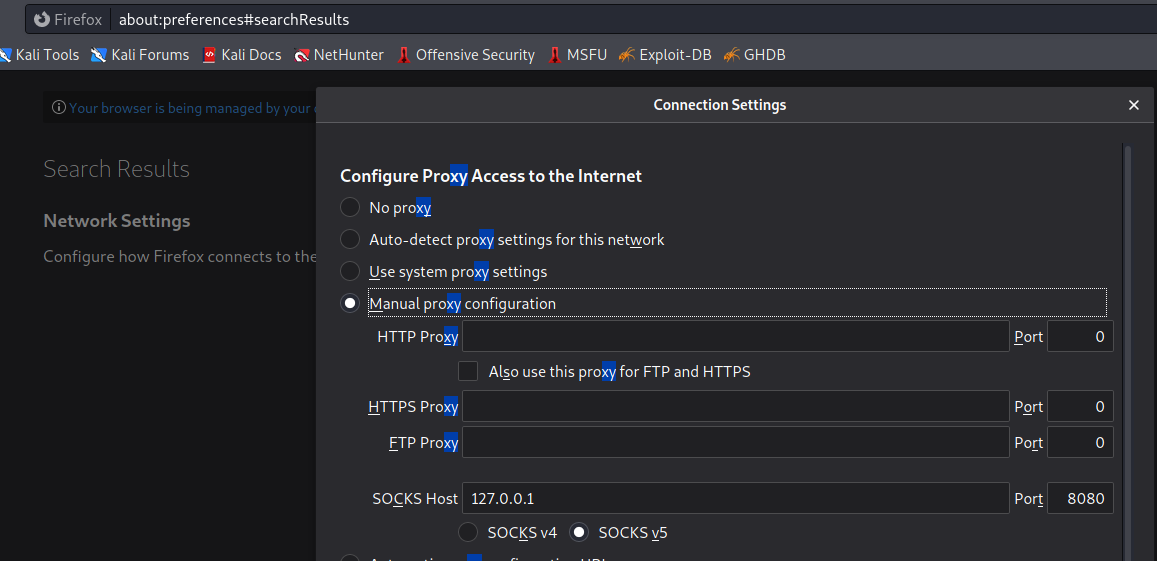
Public IP address change after using the SOCKS v5 proxy. For confirmation, I am using (https://www.whatismyip.com/)
Attacker machine before dynamic port forwarding

Attacker machine after dynamic port forwarding


Hope this article helped you to understand SSH port forwarding. :)
Comments
Post a Comment